System Design .
Antenna Design.
Image Processing Using
Open-CV.
read more
Search in Google below

PROJECTS WITH CODE
HELP SHARE IDEAS.COM
Mail us at : info@helpshareideas.com
Mobile Controlled DTMF & ARM 7 Based Robot for Multi-Application
Conventionally, wireless controlled robots user circuits, which have a drawback of limited working range, limited frequency range and limited control. Use of mobile phones for robotic control can overcome these limitations. It provides the advantages of robust control, working range as large as the coverage area of the service provider, no interference with other controllers and up to twelve controls.
Although, the appearance and capabilities of robot vary vastly, all robots share the feature of a mechanical, movables structure under some form of control. The control of robot involves three distinct phases: perception, processing, action. Generally, the perceptors are sensors mounted on the robot, processing is done by the on board microcontroller and the task is performed using motors or with some other actuators.
In the project the robot is controlled by a mobile phone that makes a call to the mobile phone stacked on the robot. In the course of a call, if any button is pressed a tone corresponding to the button pressed is heard at the other end called ‘Dual Tone Multiple frequency’ (DTMF) tone. The robot receives these tones with help of phone stacked in the robot. The received tone is processed by the microcontroller with the help of DTMF decoder IC HT9170. This IC sends a signals to the motor driver IC l293d which drives the motor forward, reverse, left and right.
The very important feature in this project is the auto trip. In the present busy world it is not convenient for a person to direct the robot everyday. It would be very useful if the robot would travel by itself and have a manual control in case of emergency. We are providing the manual control using the Microcontroller. The direction parameters such as distance, turn, are recorded. These recorded parameters are written into the Microcontroller. Hence after the manual trip the whole path will be traced by the robot.
Overview of the project
In this project, the robot is controlled by mobile phone that makes a call to the mobile phone attached to the robot. In the course of a call, if any button is pressed, a tone corresponding to the button pressed is heard at the other end of the call. This tone is called dual-tone multiple frequency (DTMF) tone. The robot perceives this DTMF tone with the help of the phone stacked in the robot.
The received tone is processed by the ATmega16 microcontroller with the help of DTMF decoder HT9170. The decoder decodes the DTMF tone into its equivalent binary digit and this binary number is sent to the microcontroller. The microcontroller is preprogrammed to take a decision for any given input and outputs its decision to motor drivers in order to drive the motors for forward or backward motion or a turn.
The mobile that makes a call to the mobile phone stacked in the robots acts as a remote. So this simple robotic project does not require the construction of receiver and transmitter units. DTMF signaling is used for telephone signaling over the line in the voice-frequency band to the call switching centre. The version of DTMF used for telephone tone dialing is known as ‘Touch-Tone’.
DTMF assigns a specific frequency 9consisting of two separate tones) to each key so that it can easily be identified by the electronic circuit. The signal generated by the DTMF encoder is a direct algebraic summation, in real time, of the amplitudes of two sine (cosine) waves of different frequencies, i.e., pressing ‘5’ will send a tone made by adding 1336 Hz and 770 Hz to the other end of the line.
Block Diagram for the proposed DTMF bases robot using ARM7 LPC2148
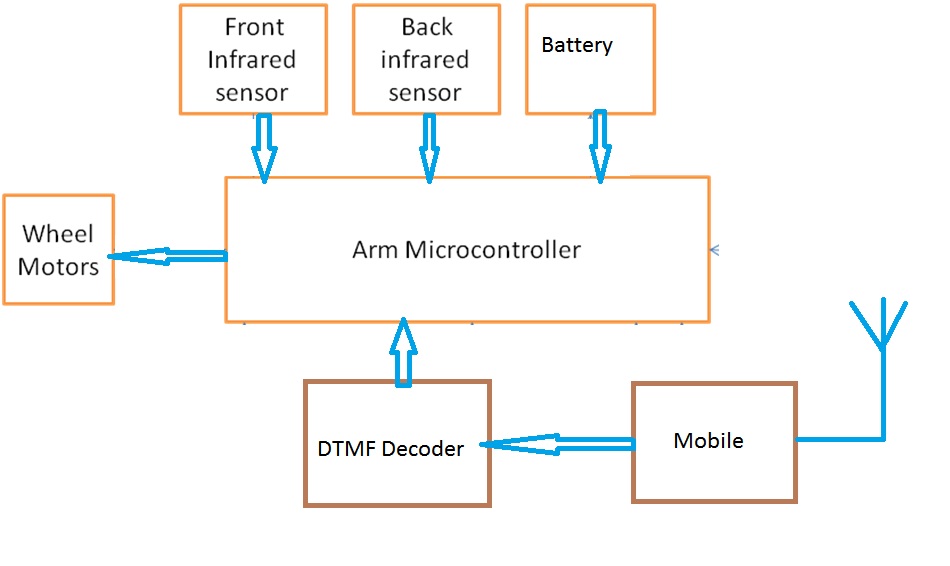
Fig 1: Block diagram
About ARM 7- LPC 2148
The LPC2141/2/4/6/8 microcontrollers are based on a 32/16 bit ARM7TDMI-S CPU with real-time emulation and embedded trace support, that combines the microcontroller with embedded high speed flash memory ranging from 32 kB to 512 kB. A 128-bit wide memory interface and unique accelerator architecture enable 32-bit code execution at the maximum clock rate. For critical code size applications, the alternative 16-bit Thumb mode reduces code by more than 30 % with minimal performance penalty. Due to their tiny size and low power consumption, LPC2141/2/4/6/8 are ideal for applications where miniaturization is a key requirement, such as access control and point-of-sale. A blend of serial communications interfaces ranging from a USB 2.0 Full Speed device, multiple UARTS, SPI, SSP to I2Cs and on-chip SRAM of 8 kB up to 40 kB, Make these devices very well suited for communication gateways and protocol converters, Soft modems, voice recognition and low end imaging, providing both large buffer size and high processing power. Various 32-bit timers, single or dual 10-bit ADC(s), 10-bit DAC, PWM channels and 45 fast GPIO lines with up to nine edge or level sensitive external interrupt pins make these microcontrollers particularly suitable for industrial control and medical systems.
Components required for the Project
- Below Components are used while designing the project
- ARM 7 LPC 2148 - 1 no.
- Infrared Sensors - 2 no.
- Basic Mobile - 1 no.
- Battery - 1 no.
- DC Motor- 2 no
- ULN 2003 IC and L293D IC -1 no
- DTMF Decoder
- Breadboard and Connecting Wires
Code for the Implementation of the Project
We have given the code in the below attached page. We will discuss about how to create a project, debug it and create a Hex file. Once Hex file is generated , how to upload it to the Arm 7 board in Tutorials Section.
< Click the link DTMF based Robot using Arm 7 to open the code for the DTMF based Robot using ARM7 LPC2148 to access the codes Page:>
Note : We will soon update tutorial page. You Can Learn how to create a Project using Arm 7 - LPC 2148 using those demos.
Editor: HelpShareIdeas.com
For giving feedback on this article please mail us at : info@helpshareideas.com
<: Click the link PROJECTS with Code to access the Latest Projects with codes Page:>
Read more




